Package Contents
Dataset
Specify the type of STAC object that URL will point to. This can be a STAC API, Catalog, Collection, Item, or FeatureCollection.
By default, this option is set to API.
Specify the STAC API, Catalog, Collection, Item, or FeatureCollection to read.
If a child Catalog or Collection is available, you can select which to fetch by clicking the browse [...] button to view any Catalogs or Collections contained by the STAC object passed into URL.
This option is not available if STAC URL Type is set to Item or FeatureCollection.
After specifying the STAC dataset, apply a date filter to narrow down results. Note that filters are most effective when a STAC API is passed in. Although filters will work on STAC Catalogs, Collections, and FeatureCollections, applying a filter can lead to a longer wait time for large datasets.
This option is not available if STAC URL Type is set to Item.
By default, this option is turned off.
Date Filter Type
Choose between Latest (default) and Date Range.
- Start Date: If the Date Filter Type is Date Range, select from the calendar, or enter a DateTime in the format YYYY-MM-DD 00:00:00.
- End Date: If the Date Filter Type is Date Range, select from the calendar, or enter a DateTime in the format YYYY-MM-DD 00:00:00.
This option is not available if STAC URL Type is set to Item.
After specifying the STAC dataset, apply a spatial filter to narrow down results. Coordinates are expected to be based on WGS84.
|
Minimum Longitude |
The minimum longitude coordinate for the dataset bounds. |
|
Minimum Latitude |
The minimum latitude coordinate for the dataset bounds. |
|
Maximum Longitude |
The maximum longitude coordinate for the dataset bounds. |
|
Maximum Latitude |
The maximum longitude coordinate for the dataset bounds. |
- Filters are most effective when a STAC API is passed in. Although filters will work on STAC Catalogs, Collections, and FeatureCollections, applying a filter can lead to a longer wait time for large datasets.
- Spatial filters are handled differently between a STAC API and non-API STAC object. When applied with a STAC API, spatial filtering is done by checking that each Item geometry intersects with the user specified bounding box. When applied with a STAC Catalog, Collection, or FeatureCollection, spatial filtering is done by checking that each Item bounding box overlaps with the user specified bounding box.
By default, this option is turned off.
Item
Select the STAC Item by clicking the browse [...] button to open the Select File From dialog.
The list of STAC Items available for reading is determined by the dataset selected and the filters applied. The Authentication parameters initially reflect the values in the reader parameters, but you can edit the parameters in the Select File From dialog to adjust the list of displayed Items.
Select the STAC Asset(s) to read by clicking the browse [...] button. Note that this list refers to the list of possible feature types.
The reader currently supports reading raster assets, (Geo)JSON assets, GeoPackages, and text files. Here is a list of supported MIME types:
- application/geo+json
- application/geopackage+sqlite3
- application/json
- application/xml
- image/jpeg
- image/jp2
- image/png
- image/tiff; application=geotiff
- image/tiff; application=geotiff; profile=cloud-optimized
- text/plain
- text/xml
Schema Attributes
Use this parameter to expose Format Attributes in FME Workbench when you create a workspace:
- In a dynamic scenario, it means these attributes can be passed to the output dataset at runtime.
- In a non-dynamic scenario, this parameter allows you to expose additional attributes on multiple feature types. Click the browse button to view the available format attributes (which are different for each format) for the reader.
A search envelope (also known as a bounding box) is a rectangular area that defines a geographic area. In FME, the easiest way to define a search envelope is to use search envelope parameters.
Defining a search envelope is the most efficient method of selecting an area of interest because FME will read only the data that is necessary – it does not have to read an entire dataset. Search Envelope parameters apply to both vector and raster datasets and can be particularly efficient if the source format has a spatial index.
Most FME readers have parameters to define the search envelope of data that is being read:
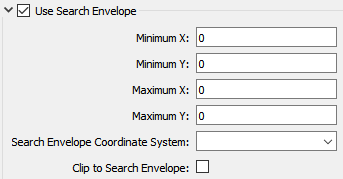
The parameters include the x and y coordinates of the bounding box as well as a parameter that defines the coordinate system.
How to Define the Bounding Box
Using the minimum and maximum x and y parameters, define a bounding box that will be used to filter the input features. Only features that intersect with the bounding box are returned. Note that the bounding box intersection is not a full geometry intersection (based on spatial relationships) that would be returned by a transformer like the SpatialFilter.
Search Envelope Coordinate System
Specifies the coordinate system of the search envelope if it is different than the coordinate system of the data. The coordinate system associated with the data to be read must always be set if this parameter is set.
If this parameter is set, the minimum and maximum points of the search envelope are reprojected from the Search Envelope Coordinate System to the reader’s coordinate system prior to applying the envelope.
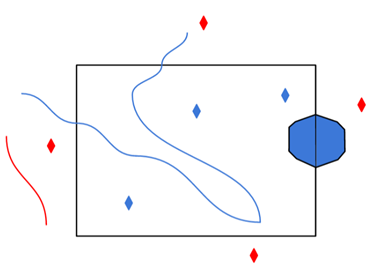
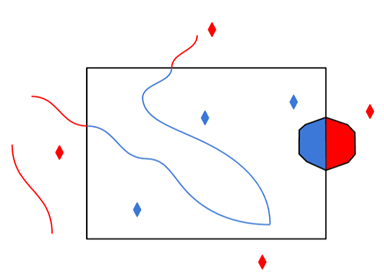
The underlying function for Use Search Envelope is an intersection; however, when Clip to Search Envelope is checked, a clipping operation is also performed.
- When checked (set to Yes), this option instructs FME to clip features to the exact envelope boundary. FME removes any portions of imported features being read that are outside the search envelope.
- When left unchecked (set to No), features that overlap the boundary will be included in their full (unclipped) form.
|
Clip to Search Envelope: No |
Clip to Search Envelope: Yes |
|---|---|
|
Any features that cross the search envelope boundary will be read, including the portion that lies outside of the boundary.
|
Any features that cross the search envelope boundary will be clipped at the boundary, and only the portion that lies inside the boundary will be read.
|
|
The search envelope includes the bounding box and the extent of the raster.
|
The search envelope includes only the area within the bounding box. The raster size will still match the bounding box, but the area without data will be filled with Nodata values to represent the absence of data, if the source raster has them. Raster Nodata may be a single value across all bands, a single value per band, or a separate alpha or transparency band that indicates the lack of data values (this is more common in images than other types of rasters).
|
Advanced
HTTPS certificate verification behavior must be explicitly enabled (set to Yes) or disabled (set to No) by this parameter.
By default, this parameter is set to Yes.